Posidyne Clutch Brakes Utilize Several Actuation Logics Designed For Specific Applications
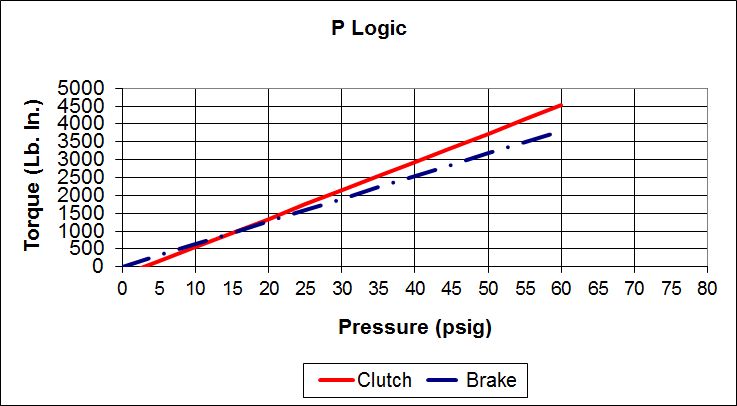
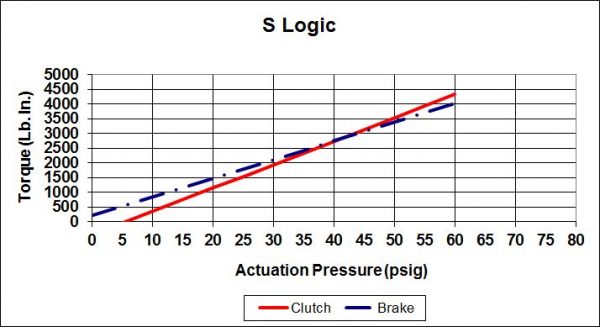
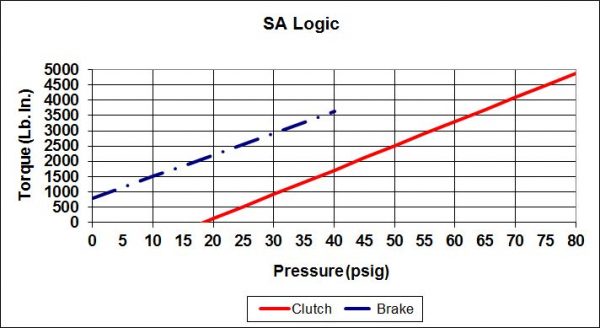
Posidyne Clutch Brake Logic is the Interaction of Clutch and/or Brake Actuation Pressure and Spring Pressure.
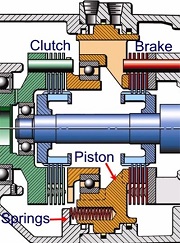
Posidyne clutch brakes are designed with a clutch and brake stack on either side of a centrally located piston. The clutch connects to the input to drive the output shaft, the brake connects to the housing to enable stopping the output shaft. To operate the clutch brake the piston is moved to the clutch side or brake side putting pressure on the corresponding friction stack causing acceleration or deceleration.
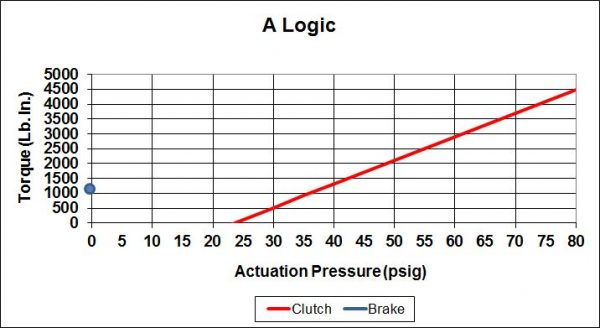
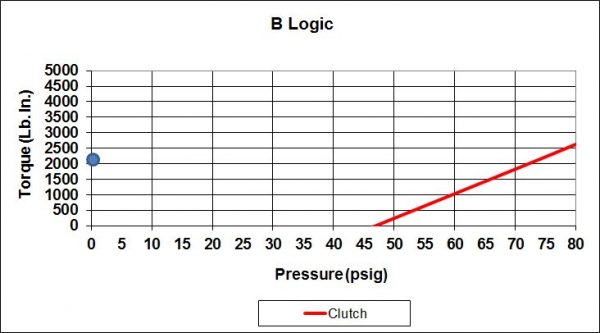
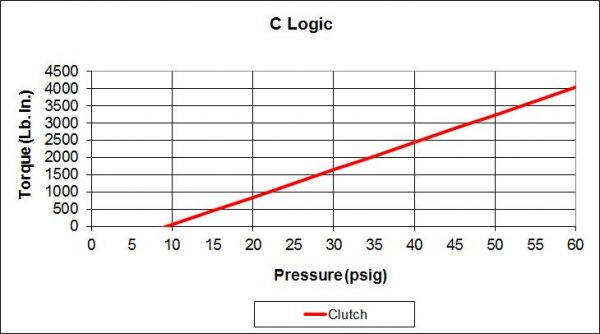
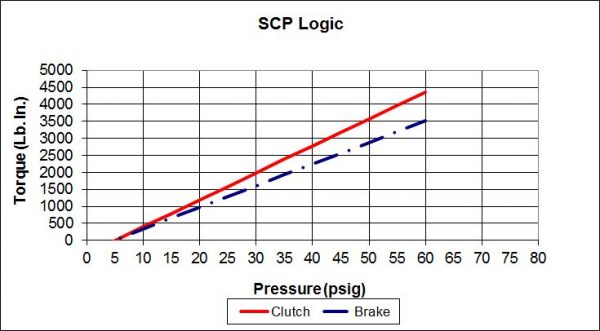
Because not all applications are the same there are 7 logic types to choose from. Some provide spring set braking for safety on vertical loads, some are for the most precise control, and some allow a neutral position enabling the drive to be rotated freely. This combination of pressure set and spring set is called logic type and is identified as S, SA, B, C, SCP, and P.
Each is the best choice for particular types of applications. The following attempts to help identify the right logic for your application.